Planning a Round Trip
This use case describes how to plan classical round trips starting at a depot and returning to it at the end of a tour.
All orders are delivered from one single depot, which is also the starting and ending point of the 's journey. Sometimes, there are some return orders. To ensure efficient use of resources, the vehicles are expected to execute multiple deliveries from or to customers.
Example | The following picture shows an example of the desired tour structure
Benefits
- Users learn how to parametrize the current use case.
- Basic insight into how to influence the course of a tour.
Prerequisites
Please ensure following prerequisites are fulfilled before you start with the use case:
- Installed and licensed PTV xTour service
- License for as many vehicles as the plan should contain
Concepts
Programming Guide
This example explains how the request has to look like in order to influence the tour structure as mentioned in the use-case description above.
First we define our locations as OffRoadRouteLocations in the default EPSG:4326 format (see RequestBase.coordinateFormat).
You could also use OnRoadRouteLocations, see the technical concept on waypoints and route legs for more information on the different types of .
Since the use case describes deliveries from and to a single depot, we define one location as depot and the others as customer sites, see Orders, Locations, and Stops for more details. Most likely the locations have specific opening intervals, which may lead to multiple tours if two locations cannot be served by the same vehicle within their opening hours.
The fleet in this example consists of one type of vehicle, with two available vehicle instances (defined by the number of vehicle ids).
Start and end location of these vehicles is the depot. To simplify the example code, we assume that the vehicles use direct distance (can be set in the distance mode of the request).
Since we do not want any other depots than the start and end depot to be involved in a tour and we do not want to return to the depot in between stops at customers, we need to activate the tour restrictions singleDepotPerTour and singleTripPerTour.
The last part of the example request are the orders, consisting of pickup and delivery orders that model the transportation of goods from the depot to a customer or from a customer to the depot. If no goods should be transported, please use visit orders instead.
We pass the request on to planTours. Once xTour has processed the request a callback is invoked which gives us access to the result of the calculation in form of a ToursResponse object.
var DepotA = {
"$type": "DepotSite",
"id": "DepotA",
"routeLocation" : {
"$type" : "OffRoadRouteLocation",
"offRoadCoordinate": {
"x": 6.113033,
"y": 49.608040
}
},
"openingIntervals": [{
"$type": "StartEndInterval",
"start": "2016-12-06T08:00:00+01:00",
"end": "2016-12-06T18:00:00+01:00"
}]
};
var Customer1 = {
"$type": "CustomerSite",
"id": "Customer1",
"routeLocation" : {
"$type" : "OffRoadRouteLocation",
"offRoadCoordinate": {
"x": 6.097412,
"y": 49.609597
}
},
"openingIntervals": [{
"$type": "StartDurationInterval",
"start": "2016-12-06T10:00:00+01:00",
"duration": "10.0"
}]
};
var Customer2 = {
"$type": "CustomerSite",
"id": "Customer2",
"routeLocation" : {
"$type" : "OffRoadRouteLocation",
"offRoadCoordinate": {
"x": 6.098742,
"y": 49.618829
}
},
"openingIntervals": [{
"$type": "StartDurationInterval",
"start": "2016-12-06T10:00:00+01:00",
"duration": "7200.0"
}]
};
var Customer3 = {
"$type": "CustomerSite",
"id": "Customer3",
"routeLocation" : {
"$type" : "OffRoadRouteLocation",
"offRoadCoordinate": {
"x": 6.115694,
"y": 49.619941
}
},
"openingIntervals": [{
"$type": "StartDurationInterval",
"start": "2016-12-06T10:00:00+01:00",
"duration": "7200.0"
}]
};
var Customer4 = {
"$type": "CustomerSite",
"id": "Customer4",
"routeLocation" : {
"$type" : "OffRoadRouteLocation",
"offRoadCoordinate": {
"x": 6.114835,
"y": 49.616771
}
},
"openingIntervals": [{
"$type": "StartDurationInterval",
"start": "2016-12-06T10:00:00+01:00",
"duration": "7200.0"
}]
};
var Customer5 = {
"$type": "CustomerSite",
"id": "Customer5",
"routeLocation" : {
"$type" : "OffRoadRouteLocation",
"offRoadCoordinate": {
"x": 6.138353,
"y": 49.607094
}
},
"openingIntervals": [{
"$type": "StartDurationInterval",
"start": "2016-12-06T10:00:00+01:00",
"duration": "10.0"
}]
};
var Customer6 = {
"$type": "CustomerSite",
"id": "Customer6",
"routeLocation" : {
"$type" : "OffRoadRouteLocation",
"offRoadCoordinate": {
"x": 6.138353,
"y": 49.593632
}
},
"openingIntervals": [{
"$type": "StartDurationInterval",
"start": "2016-12-06T10:00:00+01:00",
"duration": "7200.0"
}]
};
var Customer7 = {
"$type": "CustomerSite",
"id": "Customer7",
"routeLocation" : {
"$type" : "OffRoadRouteLocation",
"offRoadCoordinate": {
"x": 6.121702,
"y": 49.599919
}
},
"openingIntervals": [{
"$type": "StartDurationInterval",
"start": "2016-12-06T10:00:00+01:00",
"duration": "7200.0"
}]
};
var Customer8 = {
"$type": "CustomerSite",
"id": "Customer8",
"routeLocation" : {
"$type" : "OffRoadRouteLocation",
"offRoadCoordinate": {
"x": 6.105051,
"y": 49.593632
}
},
"openingIntervals": [{
"$type": "StartDurationInterval",
"start": "2016-12-06T10:00:00+01:00",
"duration": "7200.0"
}]
};
var Customer9 = {
"$type": "CustomerSite",
"id": "Customer9",
"routeLocation" : {
"$type" : "OffRoadRouteLocation",
"offRoadCoordinate": {
"x": 6.097412,
"y": 49.601094
}
},
"openingIntervals": [{
"$type": "StartDurationInterval",
"start": "2016-12-06T10:00:00+01:00",
"duration": "7200.0"
}]
};
var locations = [DepotA, Customer1, Customer2, Customer3, Customer4, Customer5, Customer6, Customer7, Customer8, Customer9];
var map = new L.Map('map', {
center: [49.61, 6.125],
zoom: 13
});
// Add tile layer to map
var tileUrl = xServerUrl + '/services/rest/XMap/tile/{z}/{x}/{y}';
var tileLayer = new L.TileLayer(tileUrl, {
minZoom: 3,
maxZoom: 18,
noWrap: true
}).addTo(map);
var markers = L.layerGroup().addTo(map);
function planSpecificTours() {
xtour.planTours({
"locations": locations,
"orders": [{
"$type": "PickupDeliveryOrder",
"id": "PDOrder1",
"quantities": [100.0],
"pickupLocationId": "DepotA",
"deliveryLocationId": "Customer1"
}, {
"$type": "PickupDeliveryOrder",
"id": "PDOrder2",
"quantities": [100.0],
"pickupLocationId": "DepotA",
"deliveryLocationId": "Customer2"
}, {
"$type": "PickupDeliveryOrder",
"id": "PDOrder3",
"quantities": [100.0],
"pickupLocationId": "DepotA",
"deliveryLocationId": "Customer3"
}, {
"$type": "PickupDeliveryOrder",
"id": "PDOrder4",
"quantities": [100.0],
"pickupLocationId": "Customer4",
"deliveryLocationId": "DepotA"
}, {
"$type": "PickupDeliveryOrder",
"id": "PDOrder5",
"quantities": [100.0],
"pickupLocationId": "DepotA",
"deliveryLocationId": "Customer5"
}, {
"$type": "PickupDeliveryOrder",
"id": "PDOrder6",
"quantities": [100.0],
"pickupLocationId": "DepotA",
"deliveryLocationId": "Customer6"
}, {
"$type": "PickupDeliveryOrder",
"id": "PDOrder7",
"quantities": [100.0],
"pickupLocationId": "Customer7",
"deliveryLocationId": "DepotA"
}, {
"$type": "PickupDeliveryOrder",
"id": "PDOrder8",
"quantities": [100.0],
"pickupLocationId": "DepotA",
"deliveryLocationId": "Customer8"
}, {
"$type": "PickupDeliveryOrder",
"id": "PDOrder9",
"quantities": [100.0],
"pickupLocationId": "DepotA",
"deliveryLocationId": "Customer9"
}],
"fleet": {
"vehicles": [
{
"ids": ["vehicle1", "vehicle2"],
"maximumQuantityScenarios":
[
{
"quantities": [10000.0]
}
],
"startLocationId": "DepotA",
"endLocationId": "DepotA"
}
]
},
"distanceMode": {
"$type": "DirectDistance"
},
"planToursOptions": {
"restrictions": {
"singleTripPerTour": true,
"singleDepotPerTour": true
}
}
}, function(toursResponse, exception) {
displayLocations();
displayTours(toursResponse.tours);
});
}
function displayLocations() {
markers.clearLayers();
for(var i = 0; i < locations.length; i++ ){
var location = locations[i];
switch(location.$type) {
case "CustomerSite":
displayCustomerSite(location);
break;
case "DepotSite":
displayDepotSite(location);
break;
default: // VehicleLocation should not be existent in this use-case
break;
}
}
}
function displayCustomerSite(location) {
var point = getLatLngOfLocation(location);
var marker = L.marker(point, {
icon: getCircleIcon(24, xServerUrl + '/dashboard/Content/Resources/Images/Showcases/circle_gray.png'),
title: location.id
}).addTo(map);
markers.addLayer(marker);
}
function displayDepotSite(location) {
var point = getLatLngOfLocation(location);
var marker = L.marker(point, {
icon: getCircleIcon(24, xServerUrl + '/dashboard/Content/Resources/Images/Showcases/circle_orange.png'),
title: location.id
}).addTo(map);
markers.addLayer(marker);
}
function getLatLngOfLocation(location) { // Only OffRoadRouteLocations are supported in this use-case
var coordinateX = location.routeLocation.offRoadCoordinate.x;
var coordinateY = location.routeLocation.offRoadCoordinate.y;
var coordinate = L.latLng(coordinateY, coordinateX);
return coordinate;
}
function getCircleIcon(size, colorUrl) {
return L.icon({
iconUrl: colorUrl,
iconSize: [size, size],
iconAnchor: [Math.floor(size / 2), Math.floor(size / 2)]
});
}
function displayTours(tours){
var bounds = new L.latLngBounds();
var layer = null;
for(var i = 0; i < tours.length; i++){
var tour = tours[i];
var latLongsOfTour = getLatLongsOfTour(tour);
if (i == 0){
layer = L.polyline(latLongsOfTour, {color: "#575757", weight: 8}).addTo(map);
}
else{
layer = L.polyline(latLongsOfTour, {color: "#2882C8", weight: 8}).addTo(map);
}
layer.bindTooltip(tour.vehicleId, {direction: 'top'});
bounds.extend(layer.getBounds());
}
map.fitBounds(bounds);
}
function getLatLongsOfTour(tour) {
var trips = tour.trips;
var latLongsOfTour = [];
var locationLatLong = null;
if (tour.vehicleStartLocationId != null){
locationLatLong = getLocationLatLongOfLocationId(tour.vehicleStartLocationId);
latLongsOfTour.push(locationLatLong);
}
for (var tripIndex = 0; tripIndex < trips.length; tripIndex++) {
var stopSequence = trips[tripIndex].stops;
for (var i = 0; i < stopSequence.length; i++) {
var locationIdOfStop = stopSequence[i].locationId;
locationLatLong = getLocationLatLongOfLocationId(locationIdOfStop);
latLongsOfTour.push(locationLatLong);
}
}
if (tour.vehicleEndLocationId != null){
locationLatLong = getLocationLatLongOfLocationId(tour.vehicleEndLocationId);
latLongsOfTour.push(locationLatLong);
}
return latLongsOfTour;
}
function getLocationLatLongOfLocationId(locationId){
for(var i = 0; i < locations.length; i++){
var location = locations[i];
if(locationId == location.id){
var coordinate = getLatLngOfLocation(location);
return coordinate;
}
}
}
planSpecificTours();
The customer sites of the request are displayed in gray, the depot sites in orange. Since the ToursResponse only contains references to the given locations, the corresponding coordinates are taken from the request. The first tour of the result is displayed in gray, the second one in blue.
Both vehicles start their tour at the depot (orange circle) and also end it there. Due to the restricted opening intervals, especially of Customer1 and Customer5, not all the orders can be executed by the same vehicle. Therefore both vehicles need to conduct a tour at same time.
Related Topics
The following topics might be relevant for this use-case.
![]() The term vehicle describes what is being routed or planned for. Vehicles are used in route calculation, distance matrix calculation and effectively also in tour planning. In route calculation, vehicle properties like overall size, weight and speed are in focus. In tour planning, it is vehicle properties like capacity and availability.
Commonly a vehicle is motorized, like a truck - including its trailer or a car. However also a bike or even a pedestrian are included in this definition.'s journey. Sometimes, there are some return orders. To ensure efficient use of resources, the vehicles are expected to execute multiple deliveries from or to customers.
The term vehicle describes what is being routed or planned for. Vehicles are used in route calculation, distance matrix calculation and effectively also in tour planning. In route calculation, vehicle properties like overall size, weight and speed are in focus. In tour planning, it is vehicle properties like capacity and availability.
Commonly a vehicle is motorized, like a truck - including its trailer or a car. However also a bike or even a pedestrian are included in this definition.'s journey. Sometimes, there are some return orders. To ensure efficient use of resources, the vehicles are expected to execute multiple deliveries from or to customers.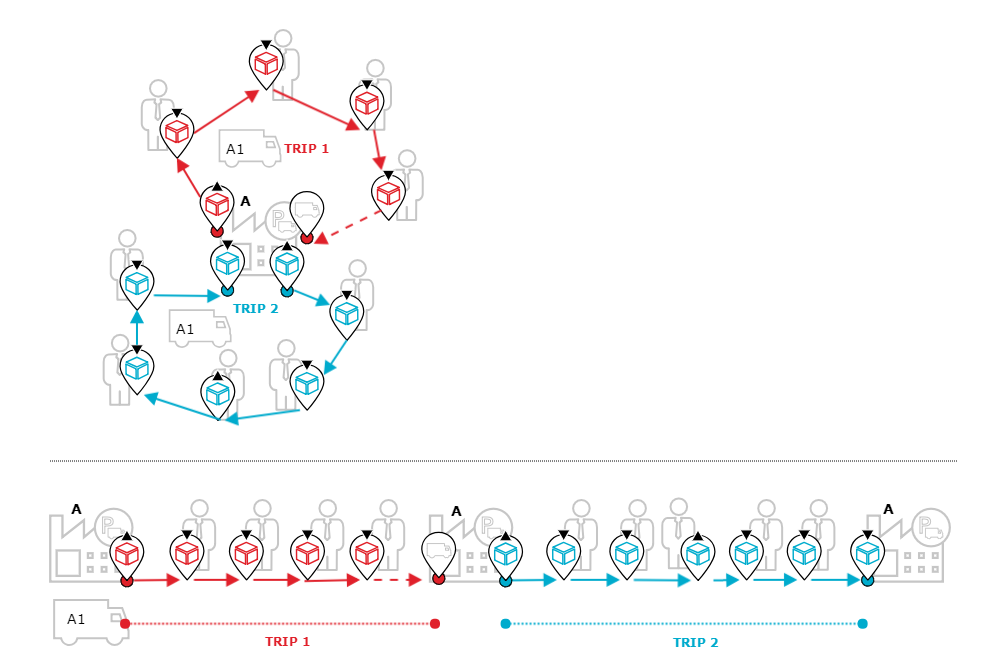
![]() A route location is the position of an object to be routed to or from, which contains additional information on how to link this position to the road network and whether or or not this position is actually reached. Route locations are used as the input for route calculation and optimization throughout PTV xServer..
Since the use case describes deliveries from and to a single depot, we define one location as depot and the others as customer sites, see Orders, Locations, and Stops for more details. Most likely the locations have specific
A route location is the position of an object to be routed to or from, which contains additional information on how to link this position to the road network and whether or or not this position is actually reached. Route locations are used as the input for route calculation and optimization throughout PTV xServer..
Since the use case describes deliveries from and to a single depot, we define one location as depot and the others as customer sites, see Orders, Locations, and Stops for more details. Most likely the locations have specific